Shelf Load Calculator
Safe Shelving Capacity Calculator
Calculate maximum safe load for your shelving based on length and load rating (e.g., "500 monkey" = 500 lbs/ft)
Common shelving types and their load ratings
| Shelving Type | Typical Load Rating (lbs/ft) | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Light-Duty Wire | 150 | Office supplies, light décor |
| Galvanized Steel (12-mm) | 300 | Small parts, seasonal stock |
| Industrial Steel (16-mm) | 500 | Bulk goods, pallets, heavy tools |
| Heavy-Duty Rack | 1000+ | Industrial equipment, large drums |
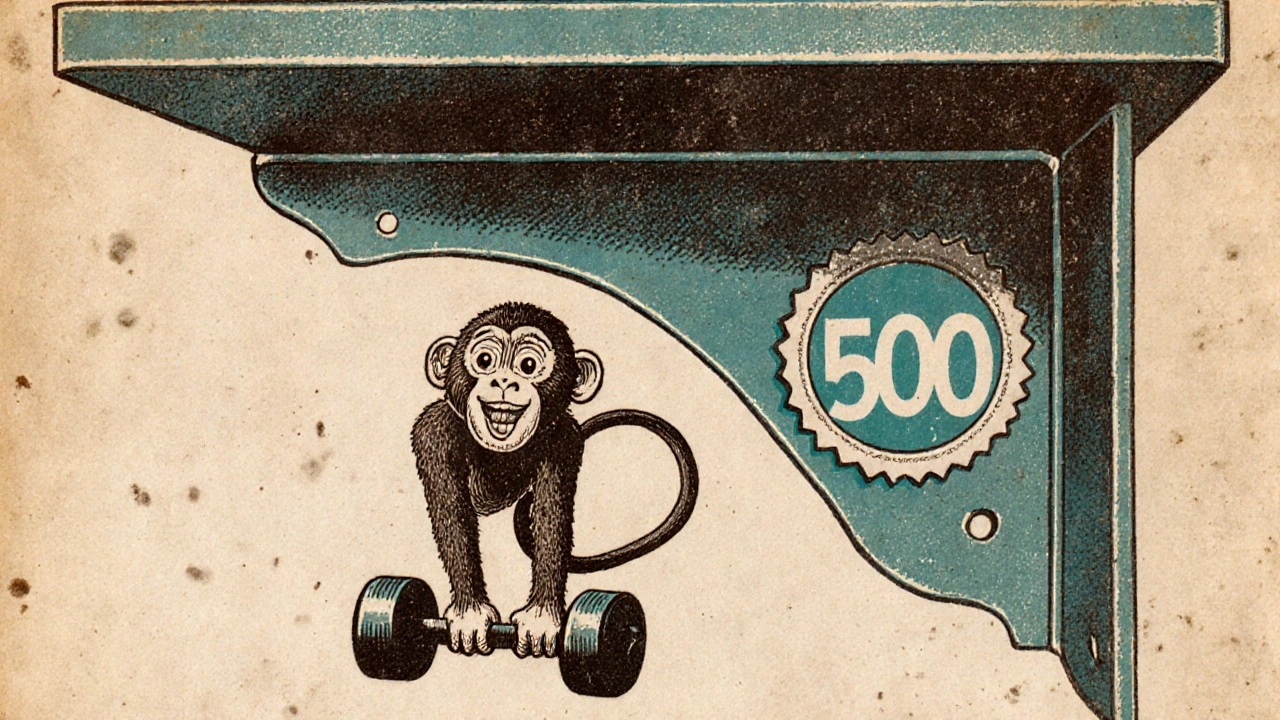
Ever walked through a warehouse and heard a worker shout, “That’s a 500 monkey!” and wondered what on earth they meant? The phrase isn’t about actual primates - it’s a piece of industry shorthand that tells you how much weight a shelf can safely hold. Understanding this quirky nickname helps you pick the right storage, avoid costly accidents, and speak the same language as the pros.
Where Did the ‘Monkey’ Nickname Come From?
Monkey is a slang term used in the shelving industry to refer to a shelf’s load rating, typically expressed in pounds per linear foot dates back to the mid‑20th century when manufacturers needed a quick way to label weight capacities on metal brackets. Early catalogues printed the number "500" next to a small cartoon of a monkey lifting a weight, implying the shelf could bear a “500‑pound” load per foot. The visual stuck, and workers began calling a 500‑pound rating a “500 monkey.” Over time, the image faded but the nickname survived, spreading across warehouse, retail, and even home‑improvement circles.
How the 500 Rating Works on a Shelf
When a shelf is marked as a 500 monkey, it means the shelf can support up to 500 pounds for every linear foot of its length, assuming the load is evenly distributed. This measurement is known as the load rating the maximum weight a shelving component can safely hold per unit length. If you have a 4‑foot shelf, the total safe load is 4 × 500 = 2,000 pounds.
Key factors that affect the rating include:
- The material of the shelf the flat, horizontal component that holds items (usually steel, aluminum, or heavy‑duty wood).
- Bracket design and spacing - closer brackets reduce bending.
- Support structure, such as pallet racking a modular storage system that uses vertical uprights and horizontal beams frames.
- Compliance with ANSI/BIFMA standards industry standards that define safety and performance for commercial furniture and storage.
Real‑World Examples on the Shop Floor
Picture a typical distribution center. A row of 6‑foot shelves labeled “500 monkey” holds pallets of canned goods. Each pallet weighs about 250 pounds, so two pallets per shelf keep the load under the 3,000‑pound limit (6 ft × 500 lb/ft). If a third pallet is added, the shelf bends, and the risk of a catastrophic failure spikes.
In a retail setting, a boutique might use a “200 monkey” shelf for delicate accessories. The lower rating reflects the lighter materials (often galvanized steel steel coated with zinc to prevent corrosion, commonly used for lighter-duty shelving) and closer bracket spacing.
Home‑improvement enthusiasts often see the term in hardware stores. A DIYer buying a set of industrial shelving for a garage will notice a sticker that reads “500 lb/ft” - the same concept, just without the monkey cartoon.

Choosing the Right Shelf Based on Load Rating
Before you click “add to cart,” think about three things:
- What will you store? Heavy items like bulk tools, lumber, or drums demand a higher rating (500 lb/ft or more). Light items-books, décor, or office supplies-can use a lower rating.
- How long will the shelf be? Longer spans increase bending forces. If you need a 10‑foot run, consider adding mid‑span supports or opting for a higher rating.
- What is the support structure? Shelves mounted on robust industrial shelving heavy‑duty storage systems designed for high load capacities frames can safely handle higher ratings than simple wall‑mounted brackets.
Use this quick checklist:
- Identify the maximum item weight.
- Multiply by the number of items per linear foot.
- Match or exceed that total with the shelf’s load rating.
If your calculation lands at 1,800 pounds per foot, look for a shelf rated at least 2,000 lb/ft (often marketed as “2‑ton monkey”).
Common Mistakes and Safety Tips
Even seasoned warehouse crews slip up. Here are the most frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Uneven loading. Placing a heavy object at one end creates a point load that can exceed the rating locally. Spread weight evenly across the shelf’s length.
- Ignoring bracket spacing. Using the same shelf on a frame with wider uprights reduces support, effectively lowering the rating.
- Exceeding the rating with dynamic loads. Items that shift during transport (boxes of parts, bulk liquids) add extra forces. Add a safety factor of 10‑15 %.
- Not checking for corrosion. Galvanized steel loses its protective coating over time, especially in humid environments. Replace corroded brackets before they weaken.
- Overlooking standards. Shelving that meets ANSI/BIFMA requirements has been tested for real‑world stresses. Look for certification tags.
When in doubt, treat the rating as a hard ceiling, not a suggestion. A shelf that fails can cause product loss, injury, and costly downtime.
Quick Reference Table
| Shelving Type | Typical Load Rating (lb/ft) | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Light‑Duty Wire | 150 | Office supplies, light décor |
| Galvanized Steel (12‑mm) | 300 | Small parts, seasonal stock |
| Industrial Steel (16‑mm) | 500 | Bulk goods, pallets, heavy tools |
| Heavy‑Duty Rack | 1,000+ | Industrial equipment, large drums |
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ‘500 monkey’ actually mean?
It’s industry slang for a shelf that can hold 500 pounds per linear foot of length, assuming the weight is evenly spread.
Can I exceed the rating for a short period?
Even brief overloads can cause permanent bending. It’s safest to stay within the rating at all times.
How do I calculate the total load for a 6‑foot shelf?
Multiply the shelf length by the load rating: 6 ft × 500 lb/ft = 3,000 pounds total capacity.
Is the ‘monkey’ term used outside the US?
It’s most common in North America, but many international warehouses have adopted it because the numeric rating is universal.
How can I tell if a shelf’s rating has dropped over time?
Look for signs of corrosion, rust, or visible bending. If brackets are loose or the finish is flaking, replace the component.
Now that you know why a 500 is called a monkey, you can read the labels on shelves with confidence, choose the right storage for your needs, and keep your workspace safe. Next time you hear a coworker shout “500 monkey!” you’ll smile, because you’ve cracked the code.